 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
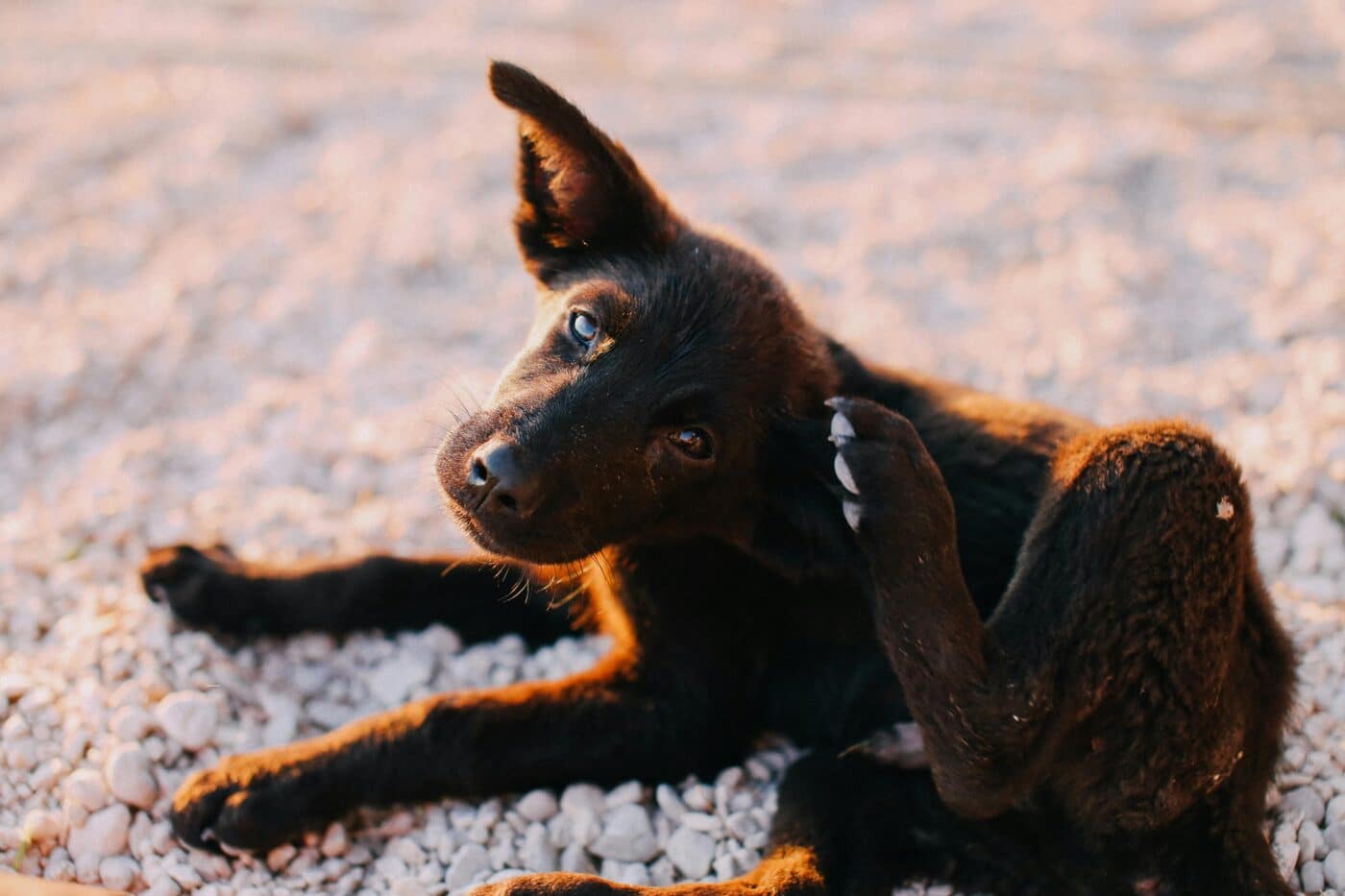
Many dog owners have observed their pets engaging in “flea biting” or “nibbling,” where a dog repeatedly bites its fur or skin. While often linked to fleas, this behavior can be caused by various other factors. Flea biting may signal discomfort, skin issues, or even behavioral concerns. Understanding the causes and motivations behind this behavior is crucial for addressing underlying problems and ensuring your dog remains healthy and comfortable. By recognizing the different triggers, pet owners can take steps to resolve this issue and improve their dog’s well-being.
Fleas and Parasites
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
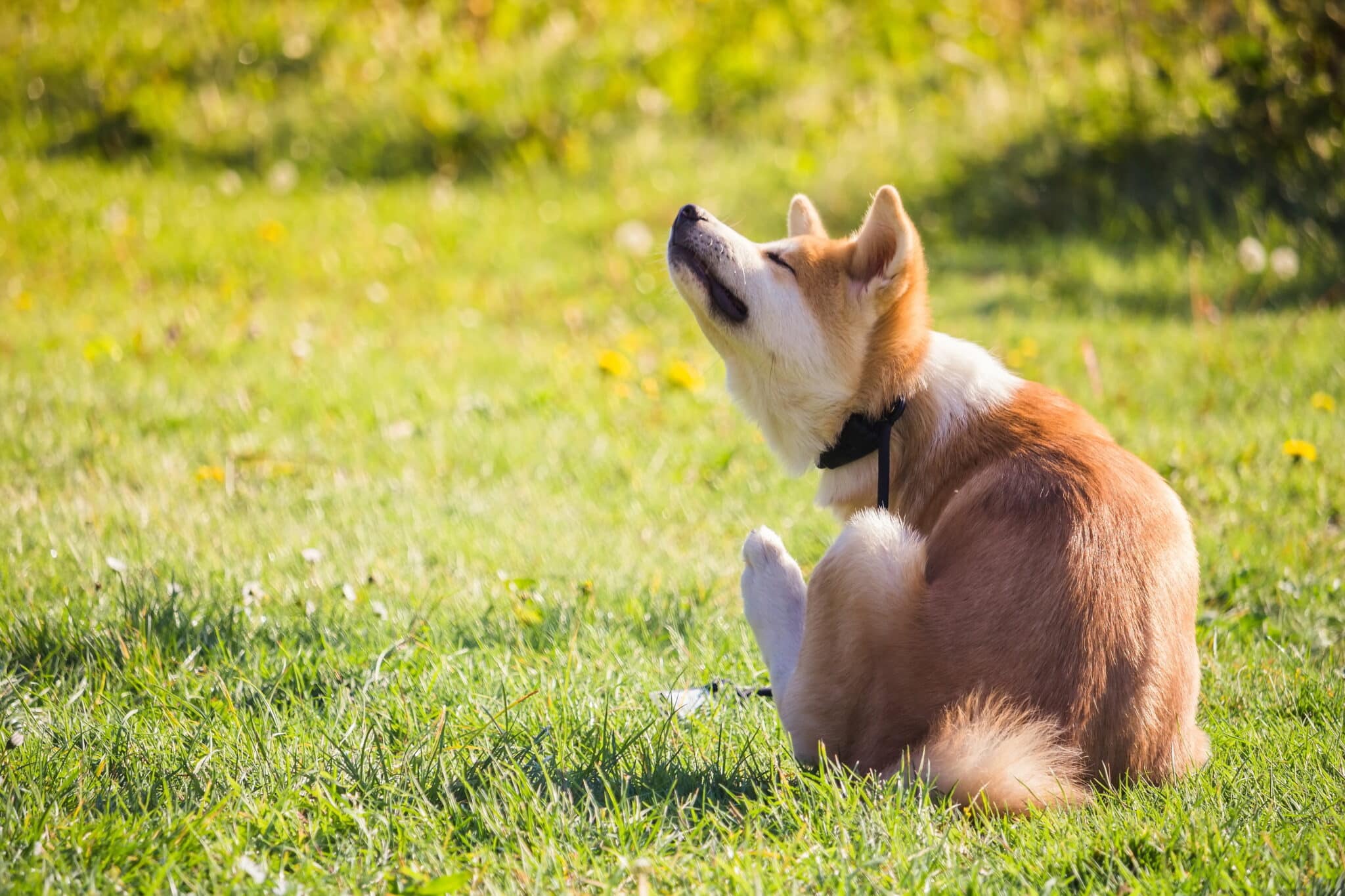
The most obvious and well-known cause of flea-biting behavior is the presence of fleas or other parasites. When fleas infest a dog’s fur, they bite and feed on the dog’s blood, which causes itchiness and discomfort. In response, the dog may nibble and bite at the irritated areas to relieve the itching. Fleas are not the only parasites that can cause this behavior; other external parasites like ticks and mites can also lead to similar reactions in dogs. Treating the infestation with flea prevention products can alleviate the discomfort and stop the biting.
Allergic Reactions to Flea Bites
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
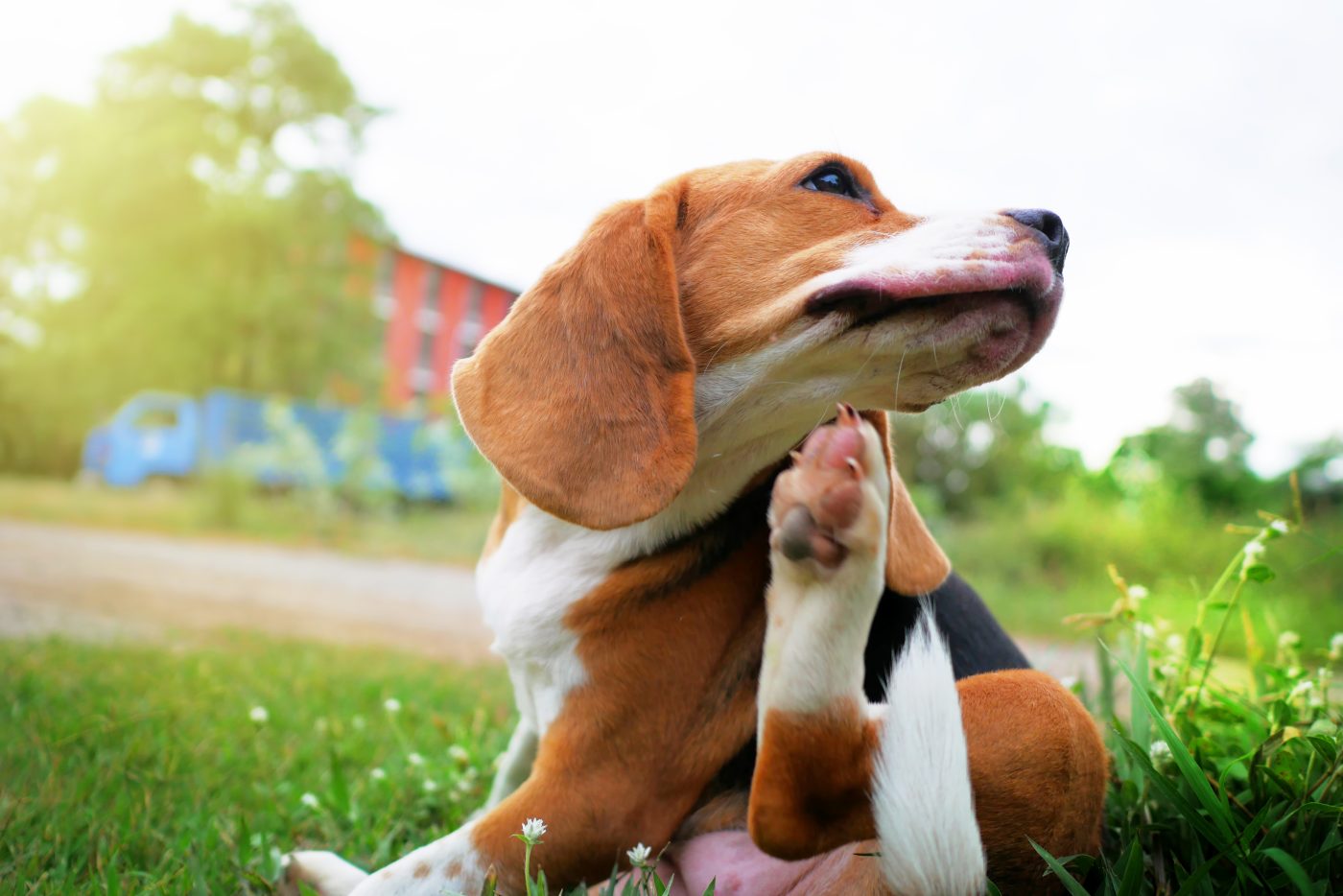
Some dogs are allergic to flea saliva, a condition known as flea allergy dermatitis (FAD). Even a flea bite can trigger an intense allergic reaction in sensitive dogs, leading to extreme itchiness and discomfort. In these cases, the dog’s flea-biting behavior may become excessive, constantly gnawing at their fur to relieve the itching. Flea allergy dermatitis can cause skin inflammation, redness, and hair loss in affected areas. Dogs with this condition often require medical treatment, such as antihistamines or steroids, to reduce the allergic reaction and stop the biting.
Dry Skin
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
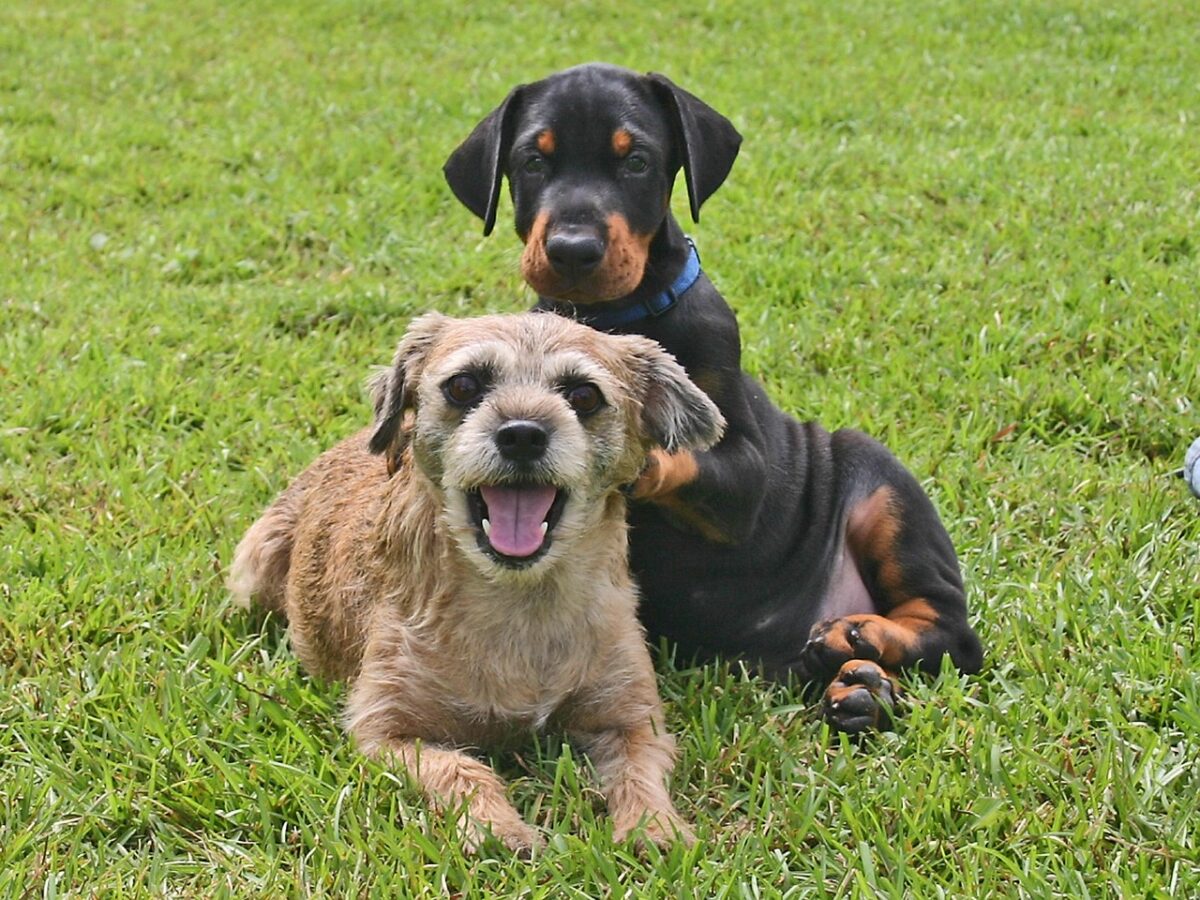
Dry skin can be another unexpected cause of flea-biting behavior in dogs. When a dog’s skin becomes dry, it can lead to itchiness and irritation, prompting the dog to bite and nibble at their fur to soothe the discomfort. Various factors, including environmental conditions, diet, or frequent bathing with harsh shampoos, can cause dry skin. Ensuring that your dog’s skin remains moisturized through proper grooming and the use of gentle, hydrating shampoos can help reduce dry skin and alleviate biting behavior.
Skin Infections
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Bacterial or fungal skin infections can cause significant discomfort and lead to flea-biting behavior. These infections can result from various factors, including allergies, poor grooming, or an existing skin condition. The presence of an infection can cause intense itchiness, prompting a dog to bite and nibble at the affected area. Sometimes, the skin may become red, swollen, or develop pustules, which only increases the dog’s discomfort. Veterinary treatment is essential for addressing skin infections, and your vet may prescribe antibiotics or antifungal medications to clear the infection and reduce the urge to bite.
Food Allergies
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Food allergies are another common reason dogs may engage in flea-biting behavior. Dogs allergic to certain ingredients in their food may develop itchy skin as a symptom, leading to excessive biting and scratching. Common allergens in dog food include proteins like beef, chicken, or dairy and grains like wheat or corn. A vet may recommend an elimination diet to identify the offending ingredient if food allergies are suspected. Switching to a hypoallergenic or limited-ingredient diet can help reduce the allergic response and stop the biting.
Anxiety or Stress
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Dogs, like humans, can exhibit nervous behaviors when anxious or stressed. For some dogs, flea biting can be a way of coping with anxiety or stress, especially when they are left alone for extended periods or experience environmental changes. This behavior, known as displacement, is a way for dogs to relieve their emotional tension. Flea biting due to anxiety may occur even in the absence of physical discomfort, and addressing the underlying stressors—such as separation anxiety, boredom, or changes in routine—can help stop the behavior.
Compulsive Behaviors
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
In some cases, flea biting may develop into a compulsive behavior, where the dog repeatedly nibbles and bites even when there is no underlying physical or emotional cause. Compulsive behaviors can be triggered by a variety of factors, including anxiety, boredom, or frustration. Once established, these behaviors can be difficult to break. They may require professional intervention, such as behavior modification therapy or the use of medications that help manage obsessive-compulsive behaviors in dogs.
Poor Grooming Habits
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Dogs not regularly groomed may develop matted fur or tangles, which can irritate the skin and cause the dog to engage in flea-biting behavior. Mats and tangles pull at the dog’s skin, causing discomfort, especially in long-haired breeds. Additionally, dirt, debris, and allergens can accumulate in a dog’s fur if not groomed properly, leading to further irritation. Regular brushing and grooming can prevent mats from forming, reduce skin irritation, and minimize the dog’s need to bite or nibble at their fur.
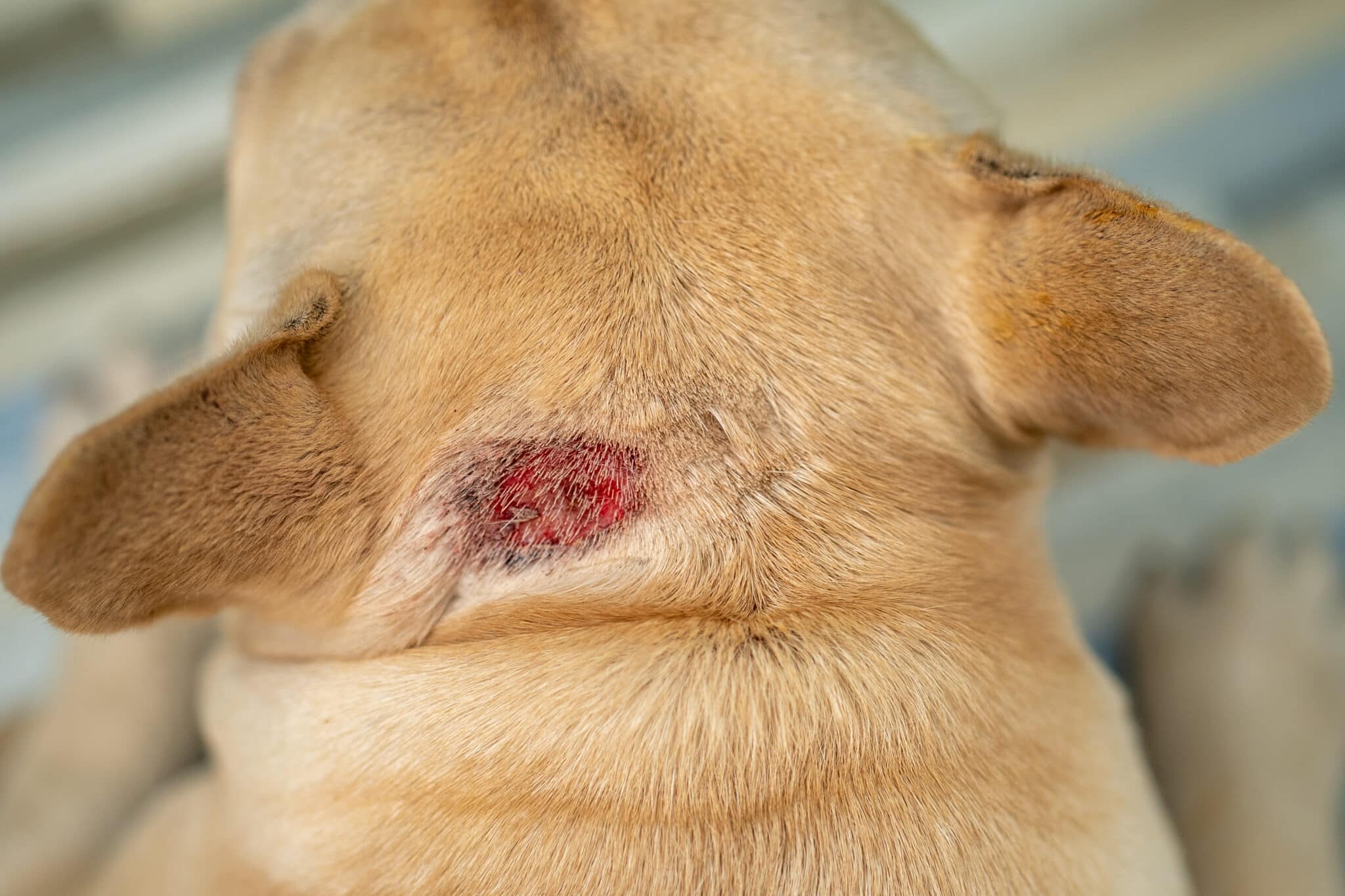
Hot Spots
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Hot spots, also known as acute moist dermatitis, are localized areas of inflamed, infected skin that can develop when a dog scratches, bites, or licks at a particular spot excessively. These painful lesions can develop quickly and cause significant discomfort, prompting the dog to continue biting at the area. Hot spots are often caused by an underlying condition such as allergies, insect bites, or skin infections. Treating the underlying cause and managing the hot spot with medications prescribed by a vet can help alleviate the pain and stop the dog from further aggravating the area.
Behavioral Boredom
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Boredom is another unexpected reason why some dogs engage in flea-biting behavior. Dogs without mental or physical stimulation may develop habits like biting or nibbling at their fur to pass the time or entertain themselves. This behavior is more likely to occur in high-energy breeds, or dogs left alone for long periods without enough exercise or interaction. Providing more enrichment through toys, games, and regular exercise can help reduce boredom-related behaviors and keep the dog engaged in healthier activities.
Flea Prevention Medications
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
In some cases, flea-biting behavior can occur after applying flea-prevention medications. While these products are designed to kill fleas and prevent infestations, some dogs may react mildly to the medication, leading to temporary irritation at the application site. This irritation may cause the dog to bite or nibble at the area where the medication was applied. If your dog exhibits this behavior after receiving flea medication, consult your vet to determine if the reaction is normal or if an alternative treatment should be considered.
Seasonal Allergies
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Just as humans experience seasonal allergies, dogs can also develop allergic reactions to pollen, grass, and other environmental allergens. These allergens can cause itchy skin, prompting dogs to engage in flea-biting behavior. When pollen levels are higher, seasonal allergies are often worse in the spring and summer months. Dogs may bite and nibble at areas of their body where the skin is particularly sensitive to allergens, such as their paws, belly, or flanks. Treating seasonal allergies with antihistamines or allergy medications can help reduce symptoms and alleviate the biting.
Flea Biting is a Social Behavior
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Flea biting is not always a sign of discomfort or irritation; in some cases, it can be a social behavior between dogs. Some dogs engage in flea biting or nibbling with their companions as a form of grooming or bonding. This behavior is common in dogs that live together and share a close bond. It is often done gently and with mutual consent and serves as a way for dogs to strengthen their social relationships. While this type of flea biting is not harmful, pet owners need to distinguish between social nibbling and biting that indicates discomfort.
Age-Related Skin Sensitivity
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
As dogs age, their skin can become more sensitive, increasing the likelihood of flea-biting behavior. Senior dogs may develop thinner skin, more prone to irritation from dry air, allergens, or parasites. Additionally, older dogs may have a reduced ability to groom themselves properly, leading to skin issues that cause discomfort. Flea biting in senior dogs may be a way of compensating for the increased sensitivity of their skin. Regular grooming, moisturizing treatments, and veterinary care can help manage these age-related skin issues.
Flea Biting and Environmental Irritants
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Environmental irritants, such as chemicals in cleaning products, lawn treatments, or perfumes, can cause allergic reactions or skin irritations in dogs. When dogs come into contact with these substances, they may develop itchy or irritated skin, leading to flea-biting behavior. Dogs are particularly sensitive to certain chemicals, and even small amounts of irritants can cause a reaction. Identifying and eliminating the source of the irritant is key to stopping the biting behavior. Using pet-safe products and limiting exposure to harsh chemicals can help prevent these reactions.
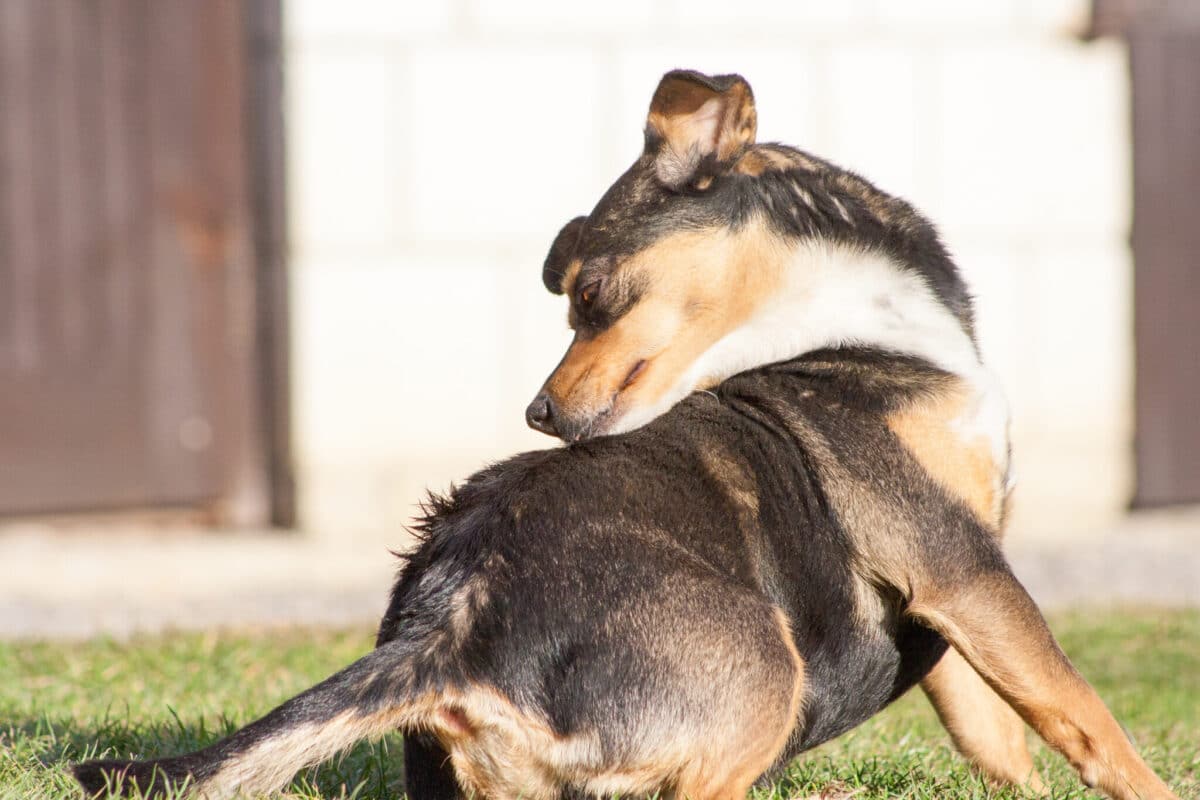
Understanding Flea Biting Behavior
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
While flea biting is often associated with parasites, it’s important to recognize that this behavior can have many causes. From allergies and anxiety to boredom and grooming issues, dogs may engage in flea biting for both physical and psychological reasons. Understanding the root cause of the behavior is essential for addressing it effectively and ensuring that your dog remains healthy and comfortable. Regular veterinary check-ups, proper grooming, and attention to your dog’s emotional well-being can all help reduce flea biting and improve your dog’s quality of life.
 Toledo, United States.
Toledo, United States.